“There’s something that doesn’t make sense. Let’s go and poke it with a stick.”
– The Doctor
Image Credits: ESA & Planck Collaboration
My research encompasses various themes, all related to computational cosmology. The following word cloud, generated from all of my publications, gives a snapshot of my research themes.

Broadly speaking, my work involves developing cosmological tools and using these to understand early universe phenomena, which often lie at the interface of cosmology and particle physics. This has allowed me to become an expert on various cosmological models, such as dark matter and neutrino models; and different cosmological datasets, like spectral distortions, Lyman-α, and gravitational waves. Additionally, I have worked on different aspect of cosmological data analysis, which has involved creating likelihood tools, producing mock data for future experiments, and performing parameter inference analyses via Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods, among others. Below you can find a brief summary of some of my main research topics. You can find more specific information about my publications on my INSPIRE, ADS, or Google Scholar profiles.
Non-cold dark matter models
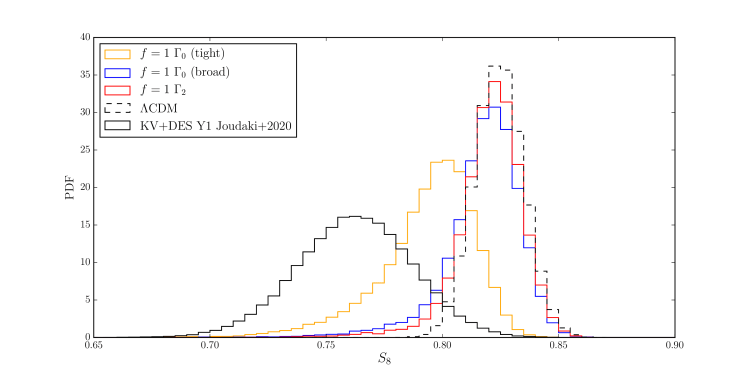
I have studied the cosmological implications of non-cold dark matter models, such as dark matter with different interactions, dark matter with cannibalistic number changing processes, and dark matter produced by the evaporation of primordial black holes. Using data such as CMB, BAO, and Lyman-α I have put state-of-the-art constraints on several of these interacting scenarios. Together with collaborators in Aachen and Cambridge, we also showed that Cannibalistic dark matter could help address the S8 tension.
Lyman-α data
In order to make use of Lyman-α data to constrain the aforementioned models, I have developed a new technique that does not require new computationally expensive N-body simulations. The approach instead relies on using a pre-existing grid of simulations covering a broad class of models, which we can interpolate in to get robust bounds from Lyman-α data. With collaborators in Aachen and Trieste, we showed the validity of this approach for dark matter interacting with dark radiation. We are currently expanding this method to cover many more dark matter interactions and other non-cold dark matter models.

Cosmological tensions
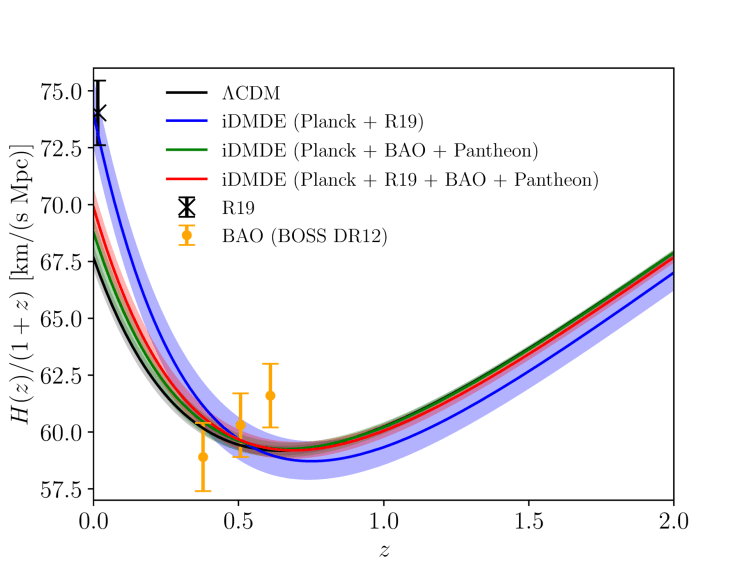
I have also analysed the possibility that these non-cold dark matter models might be able to address the cosmological tensions. I verified that some models of dark matter – dark radiation interactions can simultaneously alleviate the H0 and S8 tensions; however, the further addition of BAO+BBN or supernovae data would likely rule out this solution. On the other hand, together with a collaborator in Brussels, we showed that dark matter – dark energy interactions do not appear to solve the tension, especially when incorporating probes such as BAO and Pantheon.
Forecasts
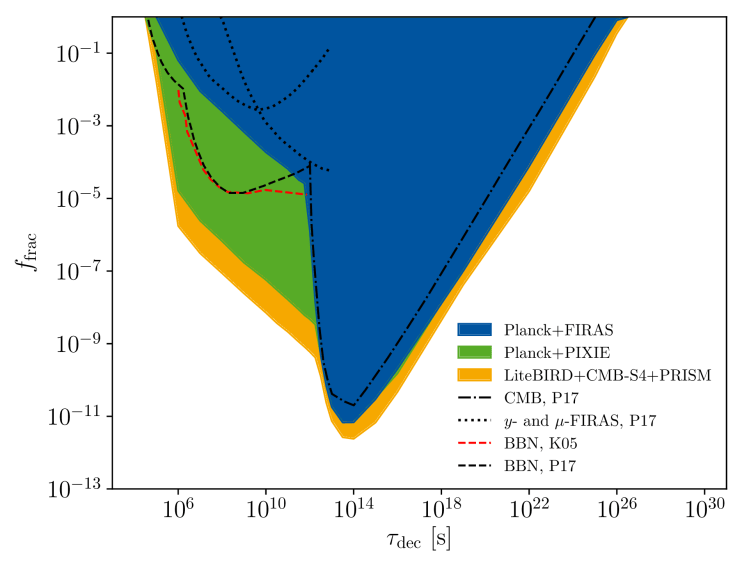
I have forecasted the constraining power of future cosmological data, such as from spectral distortions or galaxy lensing surveys. This led me to develop mock likelihoods for different missions (LiteBIRD, CMB-S4, PICO, PIXIE, PRISM), which I then used to forecast the constraints we can expect in the future for the sum of neutrino masses, decaying dark matter, and primordial black hole evaporation. With collaborators in Aachen and Manchester, we have shown that future spectral distortions missions offer a great complementarity with current and future CMB anisotropy missions.
Inflation
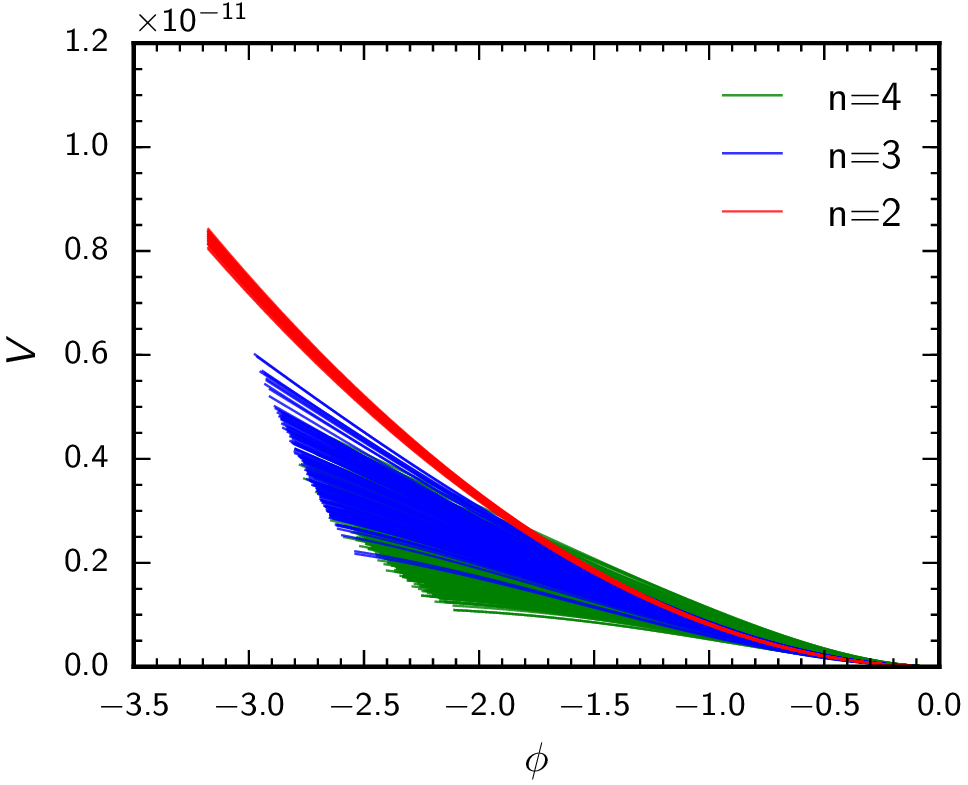
During my Master’s thesis, I implemented an efficient treatment of axion monodromy inflation in CLASS. This later led me to join the Planck collaboration during my PhD, where I looked for hints in the latest data for this model. I also performed various reconstructions of the Taylor-expanded inflationary potential, both with and without slow-roll assumptions. The results I obtained were included in the Planck 2018 Inflation paper.